The Role of Smart Contracts in Cryptocurrency
The world of cryptocurrency has experienced tremendous growth and innovation over the past decade, with the introduction of new technologies and concepts that have transformed the way we think about money and financial transactions. One of the most significant developments in the cryptocurrency space is the emergence of smart contracts, which have revolutionized the way we conduct transactions and interact with blockchain technology. In this article, we will explore the role of smart contracts in cryptocurrency, their benefits, and their potential applications.
What are Smart Contracts?
A smart contract is a self-executing program that automates the enforcement and execution of an agreement or contract between two or more parties. Smart contracts are written in code and are stored and replicated on a blockchain, which ensures their immutability and transparency. The code of a smart contract defines the rules and conditions of the agreement, and once the contract is deployed on the blockchain, it can be executed automatically without the need for intermediaries.
Smart contracts were first introduced by Nick Szabo, a computer scientist and cryptographer, in the 1990s. However, it wasn’t until the launch of the Ethereum blockchain in 2015 that smart contracts gained widespread attention and adoption. Ethereum’s smart contract platform, known as the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), allows developers to create and deploy smart contracts using a programming language called Solidity.
How Do Smart Contracts Work?
Smart contracts work by using a set of predefined rules and conditions that are encoded in the contract’s code. When a smart contract is deployed on a blockchain, it is replicated on every node in the network, ensuring that everyone has a copy of the contract and its rules. Once the contract is deployed, it can be triggered by an event or a transaction, which sets off a chain of actions that are defined in the contract’s code.
For example, a simple smart contract could be used to facilitate a bet between two parties. The contract would define the terms of the bet, including the amount of money to be wagered, the outcome of the event, and the payout structure. When the event occurs, the contract would automatically execute the payout based on the outcome, without the need for intermediaries or manual intervention.
Benefits of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts offer several benefits that make them an attractive solution for a wide range of applications. Some of the most significant benefits of smart contracts include:
- Immutable and Transparent: Smart contracts are stored on a blockchain, which ensures their immutability and transparency. Once a contract is deployed, it cannot be altered or deleted, and all parties can view the contract’s code and execution history.
- Automated Execution: Smart contracts can automate the execution of an agreement, eliminating the need for intermediaries and manual intervention.
- Reduced Counterparty Risk: Smart contracts can reduce counterparty risk by ensuring that both parties fulfill their obligations, as defined in the contract.
- Increased Efficiency: Smart contracts can increase efficiency by automating repetitive tasks and reducing the need for manual intervention.
- Cost Savings: Smart contracts can reduce costs by eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the complexity of transactions.
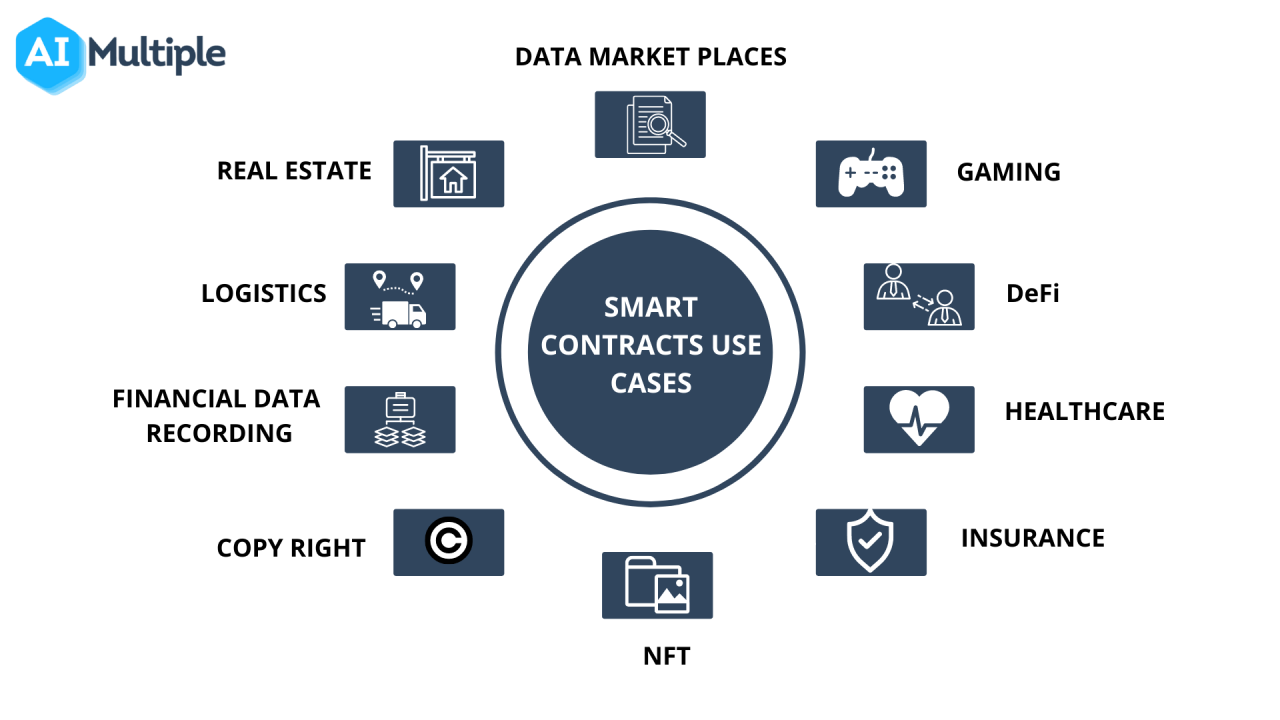
Applications of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts have a wide range of potential applications, including:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Smart contracts are used to create decentralized lending platforms, stablecoins, and other financial instruments.
- Supply Chain Management: Smart contracts can be used to automate supply chain management, including tracking and verifying the origin and movement of goods.
- Voting Systems: Smart contracts can be used to create secure and transparent voting systems, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the risk of voter fraud.
- Insurance: Smart contracts can be used to create parametric insurance contracts, which automatically payout claims based on predefined conditions.
- Gaming: Smart contracts can be used to create decentralized gaming platforms, including online casinos and poker rooms.
Challenges and Limitations
While smart contracts offer many benefits, they also face several challenges and limitations. Some of the most significant challenges and limitations include:
- Security Risks: Smart contracts can be vulnerable to security risks, including bugs and exploits.
- Scalability: Smart contracts can be limited by the scalability of the underlying blockchain, which can lead to congestion and high transaction fees.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Smart contracts are still a relatively new concept, and regulatory uncertainty can make it difficult to navigate the legal and regulatory landscape.
- Interoperability: Smart contracts can be limited by interoperability issues, which can make it difficult to integrate with other blockchain platforms and systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, smart contracts have revolutionized the way we conduct transactions and interact with blockchain technology. Their benefits, including immutability, transparency, and automated execution, make them an attractive solution for a wide range of applications. However, smart contracts also face several challenges and limitations, including security risks, scalability issues, and regulatory uncertainty. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see new and innovative applications of smart contracts, and the potential for widespread adoption and integration into mainstream industries.
Future of Smart Contracts
The future of smart contracts looks promising, with several trends and developments expected to shape the industry. Some of the most significant trends and developments include:
- Increased Adoption: Smart contracts are expected to see increased adoption, as more industries and companies begin to recognize their benefits and potential applications.
- Improved Security: Smart contract security is expected to improve, with the development of new security protocols and best practices.
- Scalability Solutions: Scalability solutions, such as sharding and off-chain computation, are expected to improve, allowing for increased throughput and lower transaction fees.
- Interoperability: Interoperability between different blockchain platforms and systems is expected to improve, allowing for seamless integration and communication between different smart contract platforms.
In summary, smart contracts have the potential to transform the way we conduct transactions and interact with blockchain technology. Their benefits, including immutability, transparency, and automated execution, make them an attractive solution for a wide range of applications. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see new and innovative applications of smart contracts, and the potential for widespread adoption and integration into mainstream industries.
Leave a Reply